 Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
 Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Year XXIX, Volume 33
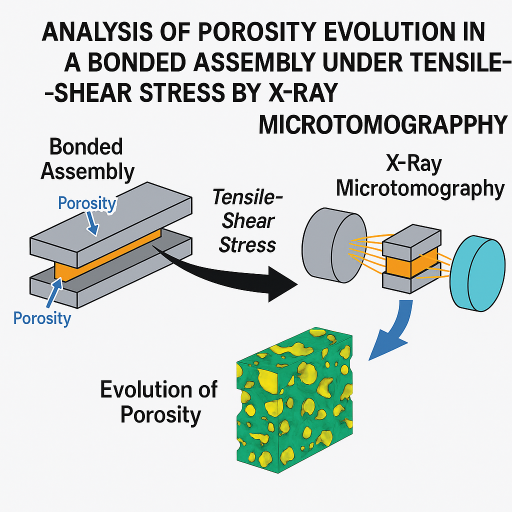
Andreea TINTATU, Claudiu BADULESCU
In the technical field of bonded assemblies, one of the main defects that can accompany adhesive joints is the presence of porosities. In this paper, the results obtained from the characterisation of the distribution of porosities in the adhesive joint using X-ray μ-tomography and the evolution of this distribution during the mechanical loading of the joint were highlighted. The aim of this work was therefore to post-process the tests performed using an X-ray μ-tomograph and to find the evolution of several parameters (porosity rate, evolution of the geometric shape of the porosities, etc.) as a function of the load applied.
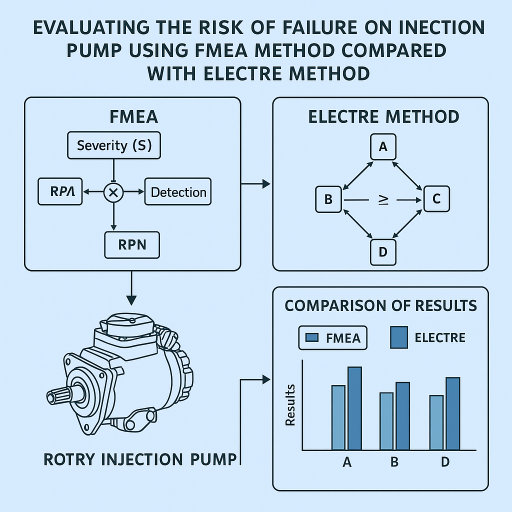
Nicoleta RACHIERU
This research is aimed at utilizing failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) which is a reliability analysis method applicable to Rotary Injection Pump design. In traditional FMEA, Risk Priority Number (RPN) ranking system is used to evaluate, the risk level of failures to rank failures and to prioritize actions. RPN is obtained by multiplying the scores of three risk factors like the Severity (S), Occurrence (O) and Detection (D) of each failure mode. RPN method can not emphasise the nature of the problem, which is multi-attributable and has a group of experts’ opinions. Furthermore, attributes are subjective and have different importance levels. In this paper, results obtained with the FMEA method are checked, using a method from decision theory, respectively the ELECTRE method, both applied for prioritizing the failures that could appear in the functioning of Rotary Injection Pump. Two case studies have been shown to demonstrate the methodology thus developed. It is illustrated a parallel between the results obtained by the traditional method FMA and ELECTRE method for determining the potential failures with the highest risk of occurrence in order to prevent them. The results show that the proposed approach somewhat modifies the obtained results and leads to the conclusion that other developments of the two methods are necessary, using fuzzy sets for the accuracy of the results.
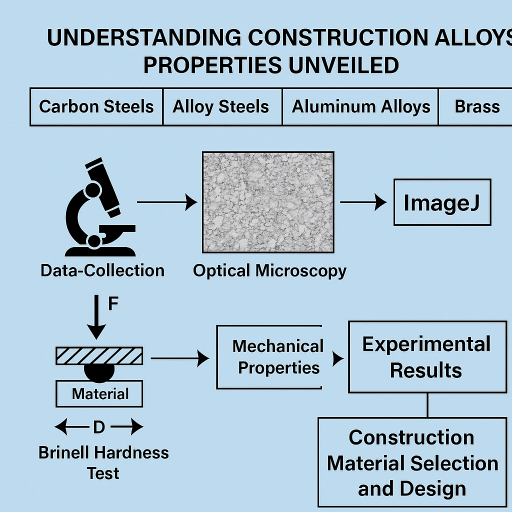
Kaoutar Chougran, Mimoun Chourak, Adriana-Gabriela Schiopu, Mohamed Nabil M. ElGabry
This article presents an experimental study on the characterization of carbon steels, alloy steels, aluminum alloys, brass, and cast iron commonly used in the construction industry. The focus is on evaluating the mechanical properties of these materials through optical microscopy and Brinell hardness testing. A series of samples representing each material type were prepared and subjected to optical microscopy analysis to examine their microstructural characteristics. The images obtained were further analyzed using ImageJ software to measure the size of various microstructural constituents. Additionally, the Brinell hardness test was conducted on each sample to quantify their mechanical strength and resistance to indentation. The experimental results provide valuable insights into the microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of these construction materials, aiding in the selection and design of appropriate alloys for specific construction applications. The findings also contribute to the broader understanding of carbon steels, alloy steels, Si-Al, brass and cast iron, offering potential improvements in construction material selection and performance.
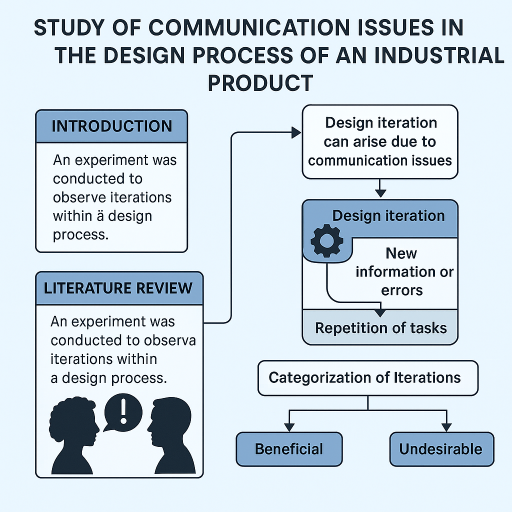
Mirela-Elena COSTELEANU, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
This paper describes an experiment conducted to observe iterations within a design process. The main purpose of this research is to investigate iterations during the design process through a laboratory experiment, aiming to comprehend their occurrence and underlying reasons. Various manifestations of iterations observed in practice are identified. This study intends to aid in categorizing iterations to differentiate between beneficial and undesirable ones. The findings from this study could potentially enhance practices within the field of engineering design.
Gina-Mihaela SICOE, Tatiana GEORGESCU, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
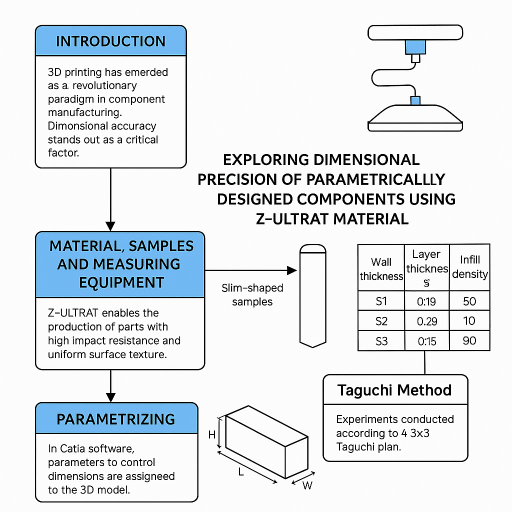
In this work, we investigated the dimensional accuracy of parametrized parts in the Catia V5 software. We adopted an experimental plan, applying the Taguchi methodology to evaluate the influence of process variables on dimensional accuracy. Process parameters such as layer thickness, infill percentage, and wall thickness were varied within the experiments, and the obtained results provided essential information regarding the influence of these parameters on the precision of parts obtained through additive manufacturing technology.
Mihai-Cătălin NITU, Adriana-Gabriela SCHIOPU, Daniela-Monica IORDACHE
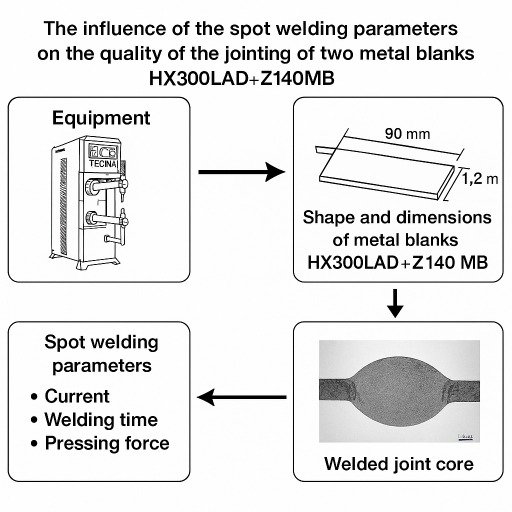
Regarding the continuing concern about the environmental impact of carbon emissions and fossil fuel consumption, the reduction of the total mass of cars without compromising mechanical and structural performance, it proved to be an important factor. Thus, the joining of sheets in the automotive industry by the method of spot welding has grown, being an ideal choice in terms of high operating speeds, default of high production volume and high degree of automation. The delivery of parts to the customer at the required quality conditions implies the optimization of the main welding parameters in the process, following the recommendations for their establishment. The paper presents the influence of the parameters of the spot welding process: intensity, welding time, pressing force on the quality of the jointing of two HX300LAD + Z140MB blanks.