

Buletin stiintific – Seria Autovehicule Rutiere



DOI: 10.26825/bup.ar.YYYY.III
Call for Papers: 2025 Issue Now Open!

Robert Marian POPA, Adrian CLENCI, Victor IORGA-SIMĂN, Rodica NICULESCU
Abstract:The problem of global warming is becoming an increasingly intense concern for all industries. In order to limit the increase in temperature to 1.5°C by 2030, according to the Paris agreement of 2015, humanity should reach zero CO2. Among the alternative fuels available now, methane gas is considered to be one of the best substitutes for fossil fuels.The main problem in using the methane gas as fuel is missing of an exclusive optimisation of the engines due to compromise in bi-fuel operations.The paper will present the engine prototype, its adaptation on a vehicle, aiming to be tested on the roller bench for emissions, as well as experimental results obtained at the engine test bed showing a comparison with a standard commercial gasoline engine.
Keywords:Natural gas, methane, CO₂ emissions, spark ignition, sustainability

Maria-Magdalena DICU, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
Abstract:This paper presents the development and characterization of ceramic coatings obtained by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) on aluminum alloys. The electrolyte used is a mixture of sodium metasilicate (Na₂SiO₃) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The resulting surfaces were characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX), and tribological testing. Additionally, correlations between structure and performance were discussed.
Keywords:PEO, coatings, surface analysis, tribological testing
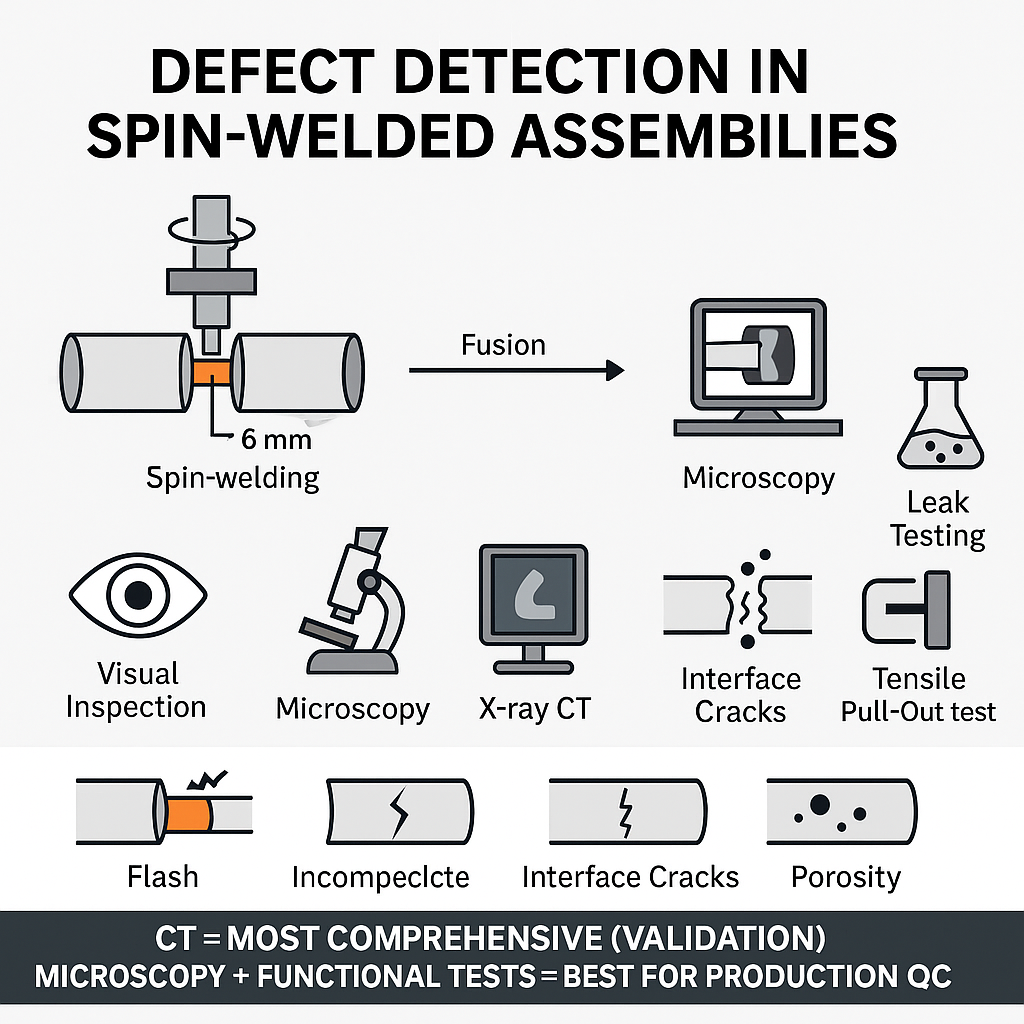
Razvan UNGUREANU, Andreea TINTATU
Abstract:Spin Welding (SW) is a solid-state joining process widely used for thermoplastic components in automotive fluid transfer systems, offering high mechanical strength, sealing integrity, and full process traceability. However, due to the internal location of the weld interface, conventional optical inspection methods cannot be applied, making defect detection challenging. This study investigates defect detection and characterization in SW tube–connector assemblies, focusing on applications in safety-critical automotive environments. Assemblies were produced using a Mecasonic 72 horizontal SW machine, with process parameters established through Design of Experiments (DOE). A comprehensive evaluation methodology was applied, combining external visual inspection, bright field and polarized light microscopy, X-ray computed tomography (CT), leak testing, and tensile pull-out testing. The analysis identified common defect types, including flash formation, incomplete fusion, interface cracks, and porosity, and correlated their occurrence with deviations in welding time, displacement, and energy input. CT scanning proved most effective for complete circumferential defect mapping, while a combination of bright field microscopy and functional tests was deemed more practical for production environments. The findings provide a technical foundation for subsequent optimization of SW process parameters to reduce or eliminate defect occurrence.
Keywords:Spin Welding, thermoplastic welding, defect analysis, computed tomography, leak testing, automotive fluid transfer
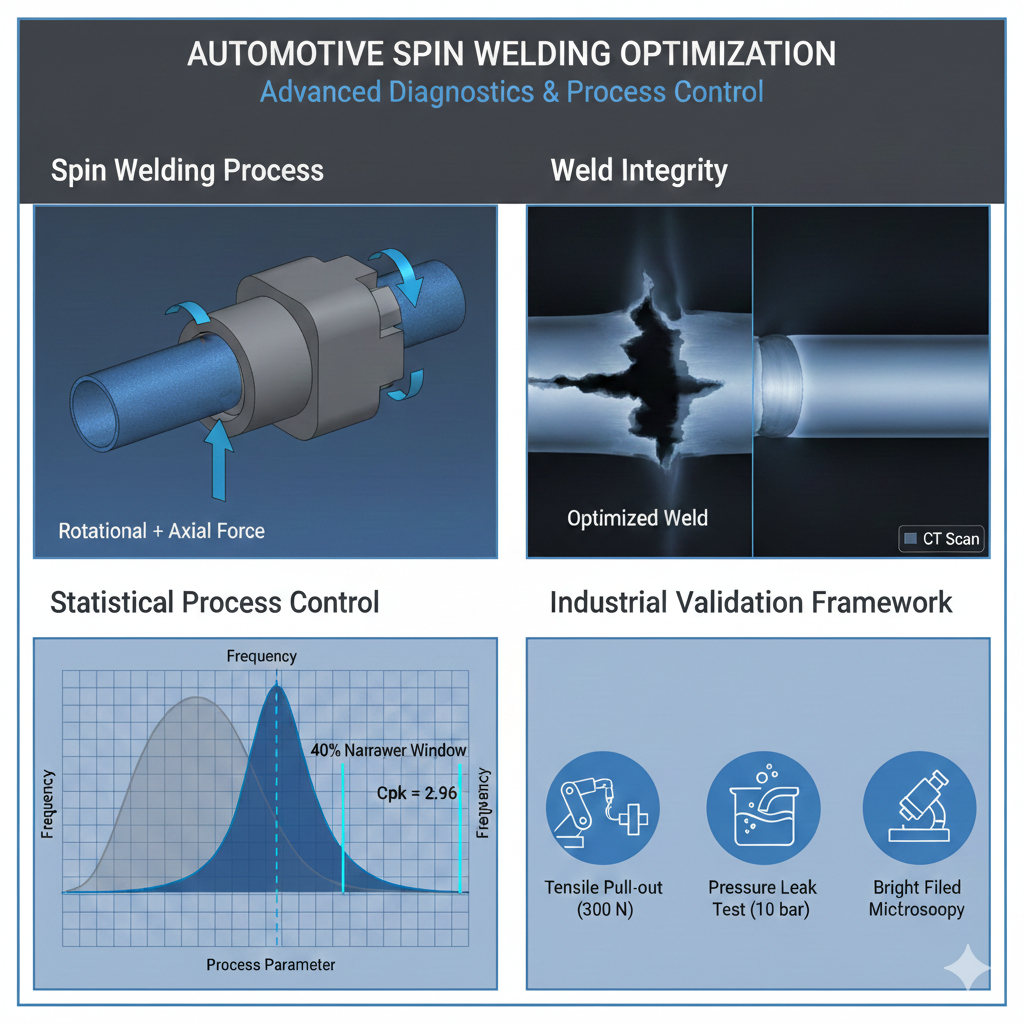
Razvan UNGUREANU, Andreea TINTATU
Abstract:Ensuring the integrity of thermoplastic tube–connector joints is essential for the reliability and safety of automotive fluid transfer systems. This work focuses on defining and optimizing spin welding parameters to minimize defect occurrence and guarantee consistent joint quality. A Design of Experiments (DOE) approach was applied on a Mecasonic 72 horizontal welding machine, testing 20 parameter sets across 200 assemblies. Results showed that only 25% of the initial parameter sets fulfilled all acceptance criteria, underlining the narrowness of the unoptimized process window. To address this, Taguchi’s loss function was combined with statistical capability studies (Cp, Cpk) performed on 100 production samples, leading to optimized parameter ranges with tolerance intervals reduced by nearly 40%. The optimized process demonstrated high robustness, with capability indices significantly above automotive requirements (Cpk ≥ 1.67). Validation through tensile pull-out tests, leak testing, and light microscopy confirmed the elimination of defects such as incomplete fusion, excessive flash, and cracks. The proposed framework provides a reliable methodology for achieving defect-free spin-welded joints, offering both statistical rigor and industrial feasibility for large-scale automotive production.
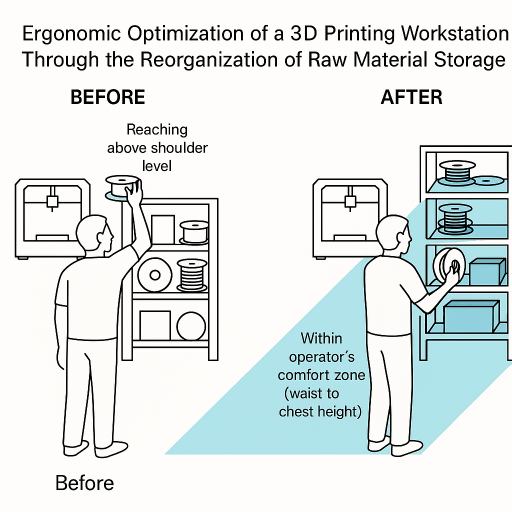
Gina-Mihaela SICOE, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
Abstract:This paper aims to analyze the ergonomic design of a workstation dedicated to the use of a 3D printer, focusing primarily on the storage and organization of raw materials used in additive manufacturing. The study is based on a real-world scenario in which the materials were initially placed randomly on shelves, without consideration for their usage frequency or weight. This disorganized arrangement led to repeated or awkward operator movements, such as reaching above shoulder level or excessive bending, which may cause discomfort or musculoskeletal disorders over time. Furthermore, this inefficient setup negatively affected operator performance. To improve the ergonomics of the workstation, we proposed a reorganization of the materials based on ergonomic principles, considering both the weight and usage frequency of the items. Heavier and less frequently used materials were relocated to the lower shelves, while lighter, frequently accessed items were positioned within the operator’s comfort zone—around waist to chest height. The goal was to reduce physical strain, enhance operational efficiency, and prevent occupational health risks. The study also includes an evaluation of the redesigned workstation using the RULA (Rapid Upper Limb Assessment) method, in order to quantify the biomechanical load in both the initial and improved configurations.
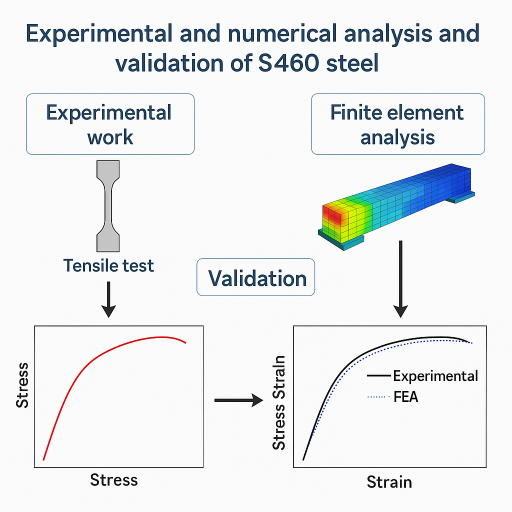
Mihai ŞTIROSU, Ştefan TABACU
Abstract:Finite elements simulation benefit from a considerable decrease in the associated expenses with an optimal design of components. Numerical models are an efficient tool for performance evaluation, monitoring of structures, damage detection, prediction of service life, and identification of optimal maintenance methods. The success of these numerical predictions is dependent on the quality of the constitutive model adopted for material. When assessing the ultimate resistance of components as fracture as a failure mode, the use of cumulative damage models is required to provide reliable results.